does ph change after autoclaving|oxidation reaction after autoclave : tv shopping Yes, sure, pH changes are frequently observed during a treatment in . To ensure optimum performance of your STATIM cassette autoclave, change the cassette seal every 500 cycles or every six months, whichever comes first. Replacement seals are available .
{plog:ftitle_list}
RX Equipment is now offering superfast Enbio Sterilizers, now available in Canada. These unique autoclaves are up to 4x faster than a typical autoclave.In fact, our new line of Enbio Sterilizers are the fastest sterilizers on the market, .
ph changes after autoclaving
So when CO2 is boiled out, the pH will increase making the media more alkaline. One is therefore meant to add the required amount of HCl to achieve the desired pH. This increase in pH that you.
© 2008-2024 ResearchGate GmbH. All rights reserved. Terms; Privacy; IP .
Yes, sure, pH changes are frequently observed during a treatment in .The pH before and after autoclaving is different. It generally falls 0.3 to 0.5 after .
Yes, sure, pH changes are frequently observed during a treatment in autoclave, as many .This paper reports that there are significant differences between initial pH levels and pH levels .The pH before and after autoclaving is different. It generally falls 0.3 to 0.5 after autoclaving. . The reaction depends on temperature, time (at elevated temperatures), the type .
oxidation reaction after autoclave
The pH change will vary based on the medium being prepared, different autoclave models, .RESULTS. Following autoclaving, pH changes were observed, particularly in the pre-autoclave .This technical article dives into why pH sensor may exhibit drift after autoclave or SIP cycles .
You have to adjust pH before autoclaving. Generally the agar shouldn't affect the pH much, so you can adjust before adding agar, which is solid anyway before autoclaving. You can check the pH with strip tests after autoclaving - just to .High temperatures during autoclaving can have a number of detrimental consequences on .After many years assuming that the filtered stock solution or buffer retained the same pH, I encountered similar results. I made a 1 M BIS-TRIS propane buffer and titrated it to pH 6.3.
It may vary according to the media, but usually we don't observe huges changes on pH before and after autoclaving. Anyway, I agree that the media is better dissolved and most close to the .
PH Method of agar after addition after auto-addition of agar claving A 5-95 il 5-42 a E 6-54 h 5-75 b T A B L E 2 . Post-autoclave pH changes in MS medium adjusted to pH 6 0 prior to autoclaving and gelled with agar ( 0-6 % ) by different methods. Means in columns not followed by the same letter are significantly different at the 1 % level MethodThe pH of the medium will likely change (usually a decrease) after autoclaving, especially in the presence of a carbohydrate source such as sucrose. The pH change will vary based on the medium being prepared, different autoclave models, sterilization times, etc., so it is advised to test the pH of the medium both before and after autoclaving to .Bhawna Tyagi. The pH before and after autoclaving is different. It generally falls 0.3 to 0.5 after autoclaving. Nutrient medium pH ranges 5-6 is suitable for growth of plants. pH higher than 6.0 makes the nutrient medium hard and less than 5 doesn't allow satisfactory gelling of agar gel. for further knowledge read this paper.
Autoclaving is a standard procedure for sterilizing nutrient media for plant tissue cultures. Most tissue cultures are grown at pH 5.2 to 5.8 with pH adjustments being made prior to autoclaving. This paper reports that there are significant differences between initial pH levels and pH levels following autoclaving, particularly in the pH range of 5.7 to 8.5. This effect is noted with and .Effect of thermal processing on the digestion of plant proteins. Kinza Mukhtar, . Rana Muhammad Aadil, in Processing Technologies and Food Protein Digestion, 2023. 16.5.4 Autoclaving. Autoclaving is a type of sterilization that uses high-pressure cooking and is usually operated at 5–15 psi and 112°C–127°C for 10–50 min. When it is applied to cereal or plant .
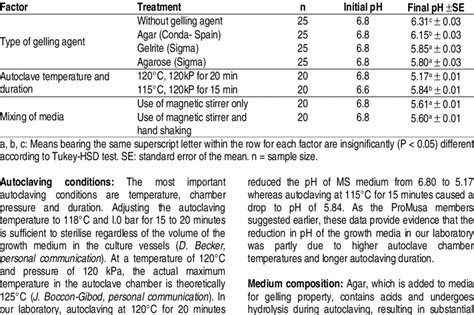
JANUARY 2008 . to 6.31 after autoclaving. However, the pH of the same medium dropped to 6.15, 5.85 and 5.80 when the . The reaction depends on temperature, time (at elevated temperatures), the type of sugar, and pH. Although caramelization often doesn’t occur during autoclaving if the autoclave is calibrated correctly and the sugar solution is retrieved promptly at the end of the run, if the conditions are right, then it can occur.
where the pH change was the difference between the pH of a chitosan solution before and after autoclaving. The amount of OH − produced by the urea hydrolysis reaction is the sum of the amount of OH − that contributed to the increase in pH of a chitosan aqueous solution and the amount of OH − that contributed to the deprotonation of amino .
autoclaving process
After autoclaving, there is a good amount of salts that precipitated out of the solution. Why did this happen? thanks, Guillermo . MgSO4 addition would not affect pH changes! Cite.High temperatures during autoclaving can have a number of detrimental consequences on culture medium, including nutrient breakdown, nutrient content changes, and pH changes, all of which can impact microbial growth. The temperature and time of sterilisation, the rate of temperature rise and fall in the autoclave, the volume of the sterilisation .color change of the processed ampoule and thinks the color change of the ampoule being removed resulted from being incubated and records the color change as a positive test. This is a situation that can be avoided by keeping a processed ampoule as your color guide for a normal color change and as a color example for a negative growth ampoule test.Prolonged autoclaving can improves the sugar caramelization and may increases the final pH of the medium, which might leads to the softening of agar (agar does not solidify at higher pH). Cite .
After autoclaving, the hydrodynamic size of Alhydrogel® increased from 342±25 nm to 516±98 nm in 10 mM of KNO 3 at pH 7.4 (Table 1, Figure S1), while their zeta potentials barely changed (Table 1). This suggested that autoclaving may .had greater gel strength at the intermediate volume of medium autoclave. In all cases, autoclaving resulted in a pH decrease of 0.2 to 0.5 pH units. Lower pH values were associated with softer gels. The type of gelling agent did not greatly affect the postautoclave pH; mean values among gelling agents were within 0.05 pH units. Postautoclave pH .After reducing agent is added to the medium, the pH is adjusted with 8 N NaOH and CO 2. The pH often changes duríng autoclaving. To attain final pH of about 7, we adjust pH with NaOH to 0.1 to 0.2 pH units above the desired autoclaving pH, then lower the pH to the value given in column 4 of the table by bubbling C0 2 through the medium. Once .I'm going to make MSA, and the manual (ISO10705-2:2000) states that pH AFTER autoclaving should be 7.2 +/- 0.5. Does anybody know if pH will change during autoclaving? MSA
to 2 units after autoclaving. Sucrose hydrolysis in tissue culture media and/or aqueous sucrose (5%) solutions containing activated charcoal (buffered to pH 5.8) was dependent on both the hydrogenion concentration (pH) and autoclaving. After autoclaving, 70%, 56% and 53% sucrose hydrolysis were respectively recorded in a 5% sucrose
When do I add the HCl or NaOH solutions, before or after autoclaving? If I change the pH of agar to a more acidic value like 3 or 4, will it solidify after autoclaving? If not, what do I need to do? Same question as question 3 but I change it to a more alkaline solution. (pH values: 10 or 11) Today I tested a set of competent E. coli cells that were prepared using a HEPES-based calcium chloride buffer solution. The solution was autoclaved as I described in the answer. I obtained a fair transformation efficiency from these .Agar can for sure solidify at pH 3.0 (lowest I tested). Problem is in fact that agar hydrolyzes or/and is modified during autoclaving at pH3.0 and therefore unable to solidify anymore. Figure 3. 1. Vessel. The vessel is the main body of the autoclave and consists of an inner chamber and an outer jacket. Laboratory and hospital autoclaves are constructed with “jacketed” chambers (see Figure 4), where the jacket is filled with steam, reducing the time that it takes to complete a sterilization cycle and reducing condensation within the chamber.
There is also no waiting period necessary to use fresh media after autoclaving, since there are no processes going on when the autoclaving was done properly. If not, you will see contaminations pretty fast.There are significant differences between initial pH levels and pH levels following autoclaving, particularly in the pH range of 5.7 to 8.5, and with time the pH of the medium drifts into the acid range. Autoclaving is a standard procedure for sterilizing nutrient media for plant tissue cultures. Most tissue cultures are grown at pH 5.2 to 5.8 with pH adjustments being made prior to .After autoclaving, there was a distinct change in color (yellow) which may suggest transformation of my glucose. . How can I change it?? . and then adjusted the pH to 7, 7.4 and 7.8. 1. 40ml .After autoclaving the solution had a pH value of 5.46 at 40° C. The twenty flasks were divided into two groups. No plantings were made in one group. The flasks in the other group . The pH changes resulting from autoclaving are shown in figure 4, curve 3. In the pH range 3-6 the 5 6 7 STARTING p H FIG. 4. pH changes in solution C without agar
autoclaving ph levels
lame de terrasse autoclave
Autoclave Maximum Registering Thermometers are for validating autoclaves by monitoring the highest temperature attained during a sterilization cycle.
does ph change after autoclaving|oxidation reaction after autoclave